Explore the challenges facing renewable energy adoption, from government policies and economic factors to public perception and infrastructure issues.In an era where global leaders are racing towards sustainable energy solutions, the United States finds itself grappling with a crucial question: Why is the U.S. so behind in renewable energy? This thought-provoking exploration delves into the multifaceted barriers slowing the adoption of renewable technologies in the country. From historical and governmental influences to economic challenges and public perception, numerous factors contribute to this dilemma. As we examine the infrastructure limitations and technological hurdles stunting innovation, we will also look beyond U.S. borders to understand why other nations are leading the charge in renewable energy implementation. Join us on this insightful journey as we uncover the complexities of renewable energy adoption in America and discuss the opportunities that lie ahead for a sustainable future.
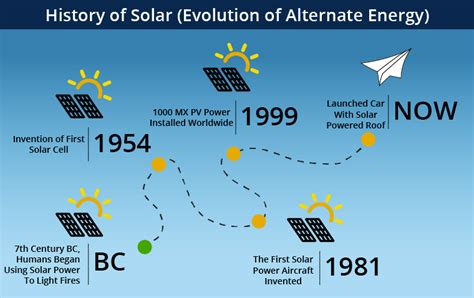
Historical Context: Why Is Renewable Energy Adoption Slow?
The slow adoption of renewable energy in the U.S. can be traced back through several decades of historical, political, and economic factors. Understanding this context provides insight into the ongoing challenges and bottlenecks in transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources.
Why is the history of energy production significant? The U.S. has long been reliant on fossil fuels, which have dominated the energy sector since the Industrial Revolution. This dependency established a robust infrastructure supporting oil, coal, and natural gas industries, making it difficult for alternative energy sources to gain a foothold.
Policy decisions made over the years have also favored traditional energy sectors. For instance, the post-World War II era saw massive investments in oil and gas, coupled with tax incentives and subsidies that reinforced the dominance of these industries. This created a cycle where fossil fuels became deeply embedded in the American economy and culture.
Additionally, the U.S. government’s approach to energy crises, such as the oil embargo of the 1970s, often resulted in a short-term focus on energy independence rather than a long-term strategy for adopting renewable sources. Even during periods of energy scarcity, the solutions often emphasized increasing domestic fossil fuel production rather than investing in renewables.
| Time Period | Key Events | Impact on Renewable Energy Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Revolution | Rise of fossil fuel dependency | Established a strong fossil fuel infrastructure |
| Post-World War II | Massive investments in oil and gas | Limited financial support for renewable energy |
| 1970s-1980s | Energy crises and market volatility | Short-term fixes over long-term renewable strategies |
Several historical decisions and societal habits have contributed to the sluggish pace of renewable energy adoption in the U.S. As the world shifts towards more sustainable practices, it is essential to recognize and learn from these past challenges to effectively move forward.
Government Policies: Why Is There Limited Support for Renewables?
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the landscape for renewable energy adoption. Despite the pressing need for a transition to cleaner energy sources, the U.S. has faced limitations in comprehensive support for renewable technologies. Here’s a breakdown of key factors contributing to this situation:
- Inconsistent Legislation: One major issue is the inconsistency in renewable energy policies across different states and at the federal level. This patchwork of regulations creates uncertainty for investors and developers, making it challenging to commit resources to renewable energy projects.
- Tax Incentives: While there are some tax incentives available, they are often temporary and subject to political changes. This leads to fluctuations in the market, where investors are unsure about the viability of long-term projects.
- Lobbying and Political Influence: The fossil fuel industry holds significant lobbying power in the U.S. government. This influence often results in policies that favor traditional energy sources over renewable options, stalling progress.
- Funding and Resources: Limited public funding for renewable energy research and development means that innovative technologies struggle to receive the necessary support to scale and become viable alternatives.
The question of why is there limited support for renewables is intricately tied to the complexities of government policies, which can either foster or hinder the growth of the renewable energy sector. Understanding the interplay of these policies is essential for developing effective strategies to overcome the barriers to renewable energy adoption in the U.S.
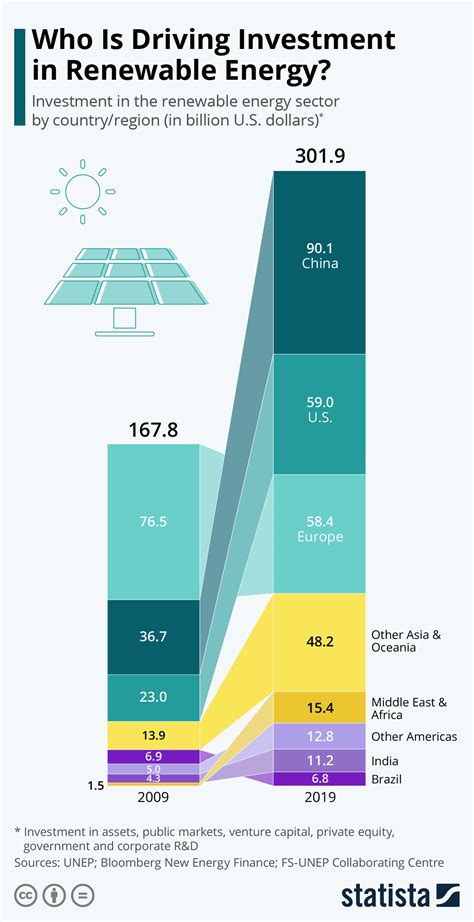
Economic Factors: Why Is Renewable Energy Investment Lagging?
Investment in renewable energy in the U.S. faces several economic challenges that contribute to its slower adoption rates compared to other countries. One primary factor affecting this investment is the fluctuating costs associated with renewable technologies. While the costs of solar and wind energy have significantly decreased, the initial capital required for infrastructure development and installation can still be a barrier for many investors. This leads to a hesitancy to commit large sums to projects that may take years to yield returns.
In addition, the renewable energy sector often competes with established fossil fuel industries that benefit from existing subsidies and entrenched market positions. These fossil fuel industries typically enjoy lower operational costs due to established supply chains and a long history of infrastructure investment. This disadvantage can dissuade potential investors who may favor more stable and historically profitable sectors.
Moreover, there is a lack of coherent long-term economic policies that consistently support renewable energy growth. Frequent changes in government policies—such as tax credits, tariffs, and regulations—create an unpredictable investment environment. These fluctuations can lead to uncertainty, making it challenging for businesses and investors to plan for the future, ultimately weakening the financial prospects for renewable energy projects.
Another significant issue lies in the financial backing available for renewable projects. Unlike fossil fuels, which have access to extensive traditional financing options, many renewable energy projects struggle to secure necessary funding. This lack of robust financing can stall innovations and projects that could help the U.S. better align with global trends toward sustainable energy.
Public funding for renewable energy initiatives lags behind countries that have made substantial commitments to green energy. The lack of government investment combined with the resistance from traditional energy sectors creates a landscape where economic incentives for renewable energy remain limited. All of these issues contribute to the overarching question: Why is renewable energy investment lagging in the U.S. compared to international counterparts? Addressing these economic barriers is crucial for enabling a significant shift toward renewable energy adoption in the future.
Public Perception: Why Is There Skepticism Towards Renewable Technologies?
Public perception plays a crucial role in shaping the future of renewable energy in the U.S. Despite advancements in technology and a growing body of evidence supporting the benefits of renewables, many individuals remain skeptical about their efficacy and reliability. This skepticism can be attributed to a variety of factors:
- Traditional Energy Dependence: A significant portion of the population has long-standing ties to fossil fuels, both culturally and economically. This historical dependence creates a resistance to change and skepticism about alternative energy sources.
- Misinformation: The prevalence of misinformation surrounding renewable technologies can cloud public understanding. Misleading claims about the efficiency and reliability of renewables lead many to question their viability.
- Initial Costs: Despite long-term savings, the upfront costs associated with installing renewable technologies, like solar panels, can deter individuals. This perception of high initial investment often overshadows potential long-term benefits.
- Concerns Over Weather Dependence: Many people worry that renewable resources such as solar and wind are too dependent on weather conditions, resulting in inconsistent energy supply. This belief can undermine confidence in their reliability.
- Lack of Awareness: Limited understanding of how renewable technologies work and their potential benefits contributes to hesitancy. Many individuals simply may not be informed about the advancements being made in renewable energy.
Addressing these concerns requires a concerted effort in education and outreach, demonstrating how renewable technologies are not only feasible but also necessary for sustainable development. Fostering an informed public can pave the way for broader acceptance and adoption of renewable energy initiatives.
Infrastructure Challenges: Why Is Grid Adaptation Necessary for Renewables?
The current electrical grid in the United States faces significant challenges in adapting to the increasing share of renewable energy sources. As we explore the question of why is grid adaptation necessary for renewables, several key factors emerge.
First and foremost, traditional energy systems are built around centralized power generation, primarily from fossil fuels. This structure poses a challenge as the U.S. seeks to integrate more decentralized renewable sources like solar and wind. These energy sources are often intermittent, meaning their output can vary significantly, which makes reliable grid management essential.
Another critical aspect is the existing transmission infrastructure, which is not always equipped to handle the distributed nature of renewable energy. Many regions lack the necessary high-voltage transmission lines that can transport renewable energy from remote locations—such as wind farms in the Midwest and solar arrays in the Southwest—back to urban centers where the demand is highest. Without this infrastructure, the effectiveness of renewable resources diminishes significantly.
To illustrate the disparities, here’s a brief comparison of the U.S. electricity transmission capability versus some leading countries in renewable energy:
| Country | Renewable Energy Capacity (GW) | High-Voltage Transmission Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 300 | Developing, high regional disparity |
| Germany | 122 | Well-developed, supports renewables |
| China | 1,200 | Extensively developed, rapid expansion |
Furthermore, the adaptation of smart grid technologies is vital. These technologies enable better demand-response mechanisms, enhance efficiency, and improve the overall stability of the grid. However, the implementation of such technologies requires significant investment and coordination among various stakeholders, including federal and state governments, utility companies, and private sector players.
Addressing the question of why is grid adaptation essential for renewable energy is central to overcoming its infrastructure challenges. Without substantial investments in modernizing the grid and building adequate transmission capabilities, the U.S. risks falling further behind in the global renewable energy race.
Technological Barriers: Why Is Innovation Key to Renewable Energy Growth?
Innovation is critical to overcoming the numerous why is challenges associated with renewable energy growth. Without advancements in technology, the transition to a sustainable energy future can stall. Here are some key factors that highlight the importance of innovation:
- Efficiency Improvements: Innovative technologies can significantly enhance the efficiency of renewable energy systems. For example, advanced solar panels and wind turbine designs can generate more energy from the same resources, making renewables more competitive with fossil fuels.
- Cost Reductions: New technological developments often lead to lower manufacturing and operation costs. As renewable technologies become cheaper, they attract more investment and adoption, reducing the financial barriers currently in place.
- Energy Storage Solutions: One of the biggest hurdles for renewable energy is its intermittent nature. Innovations in energy storage, including batteries and other storage methods, are vital for ensuring a consistent energy supply, addressing the why is issue of energy availability when sunlight or wind is not present.
- Integration with Existing Infrastructure: Developing technologies that allow for better integration of renewable energy sources with the current energy grid is crucial. This includes smart grid technologies that can efficiently manage the flow of energy and reduce waste.
- Decentralization of Energy Production: Innovative distributed energy systems can empower local communities to generate and manage their renewable energy. This not only fosters energy independence but also aligns with the growing trend of consumer engagement in the energy market.
Addressing these technological barriers through innovative approaches is essential for the growth of renewable energy in the U.S. To move forward effectively, stakeholders must focus on fostering research and development, incentivizing breakthrough technologies, and building robust infrastructure to support renewable energy systems. Without a concerted effort in innovation, the U.S. risks falling further behind in the global renewable energy landscape.
Comparative Analysis: Why Is the U.S. Outpaced by Other Nations?When considering the renewable energy landscape globally, the question arises, why is the U.S. lagging behind other nations in adopting renewable technologies? Several key factors contribute to this comparative disadvantage.
Firstly, countries like Germany and China have heavily invested in renewable energy infrastructure and technology over the last few decades. Germany’s commitment to its Energiewende (energy transition) has made it a leader in wind and solar power, while China has become the world’s largest manufacturer of solar panels. These nations have prioritized renewable energy both politically and financially, creating an ecosystem that fosters innovation and adoption.
Secondly, international policies and cooperation play a significant role. Many European countries operate under cohesive regulatory frameworks that promote renewable energy across borders. This collaboration enables knowledge sharing and resource pooling, leading to faster advancements and implementations of green technologies. In contrast, the fragmented political landscape in the U.S. often complicates unified action on climate and energy policy.
Investment is another critical area where the U.S. is being outpaced. Nations that lead in renewable energy have reallocated substantial portions of their public and private investments into the sector. In the U.S., while there has been increasing interest, investments in renewable technologies still lag behind fossil fuel sectors, primarily due to traditional energy lobbies and economic frameworks that favor non-renewable resources. Thus, the cost-competitiveness of renewables remains a challenge when compared globally.
Furthermore, education and public awareness in countries leading in renewable energy is often more robust. Citizens are more informed about the benefits of renewable resources, spurring private investments and community initiatives. In the U.S., misperceptions and a lack of understanding of renewable technologies continue to hinder broader societal support, which is crucial for scaling up renewable projects.
Technological advancements and research and development (R&D) are vital in this context. While the U.S. has major research institutions, funding and focus on the transition to renewable sources can be inconsistent. Other countries consistently funnel significant resources into R&D aimed at innovation in renewables, enhancing efficiency, and reducing costs. This has given them an edge in developing groundbreaking technologies that the U.S. then has to play catch-up with.
The reasons why is the U.S. outpaced by other countries in renewable energy are multifaceted, including investment strategies, policy coherence, public perception, and a stronger commitment to R&D. Addressing these areas will be essential for the U.S. to improve its standing in the renewable energy arena.
Frequently Asked Questions
Several factors contribute to the U.S. lagging in renewable energy, including political resistance, lack of policy incentives, a historically entrenched fossil fuel industry, and issues related to infrastructure and grid modernization.The political climate significantly influences renewable energy policies and investments. Leadership that prioritizes fossil fuels or deregulation can hinder renewable energy initiatives, while supportive governments can drive progress through incentives and legislation.Public awareness and perception of renewable energy technologies are crucial. A lack of awareness about the benefits and availability of renewables can result in lower consumer demand and inadequate policy support.Yes, geographical factors such as climate, land availability, and natural resources directly impact the feasibility and efficiency of renewable energy installations, such as solar and wind farms, across different regions.Upgrading the electrical grid to better integrate renewable sources, improving energy storage capabilities, and developing transmission networks to connect regions with renewable potential to urban centers are vital infrastructure changes for better implementation.The fossil fuel industry has significant lobbying power and financial resources that can sway policy decisions, often resulting in regulations that favor traditional energy sources over renewables, thus slowing the transition.Increasing federal and state-level incentives for renewable energy projects, investing in research and development to reduce costs, and creating more robust policies that promote sustainable practices are key steps to accelerate the transition to renewables.