Explore the fundamentals of wind energy, its conversion into electricity, benefits, challenges, global trends, and future innovations in sustainable power generation.Wind Energy: How Does It Work?
In an era where sustainable power solutions are more crucial than ever, wind energy stands out as a clean and abundant resource. Harnessing the natural power of the wind, this renewable energy source contributes significantly to reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change. Understanding how wind energy works is essential for both consumers and businesses looking to transition to greener energy sources. In this article, we will delve into the fundamental principles of wind energy, explore how wind turbines convert kinetic energy into electricity, and discuss the factors that influence energy generation, including wind speed. Additionally, we will highlight the benefits of wind energy, address the challenges in its production, and look at the global trends and future innovations shaping this vital industry. Join us as we uncover the transformative potential of wind energy for a more sustainable future.
Wind Energy: The Basics Explained
Wind energy is one of the most promising sources of renewable energy available today. It harnesses the kinetic energy produced by wind and converts it into usable power. This process is fundamental to the production of electricity and offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
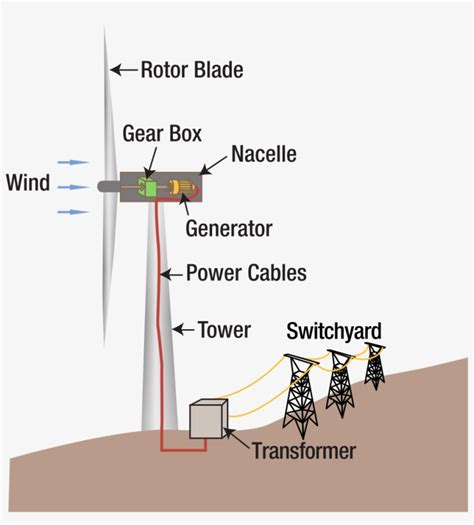
The mechanics behind wind energy involve several key components. Wind turbines are the primary devices used to capture this energy. When wind passes over the blades of a turbine, it causes them to spin. This rotation drives a generator, which then converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. The efficiency of this conversion can significantly impact the overall energy output.
Additionally, the location of wind turbines is crucial for maximizing energy capture. Areas with consistent and strong winds, such as coastal regions, elevated terrains, and open plains, are ideal for wind farms. However, the environmental impact, aesthetics, and wildlife considerations are critical factors that need to be carefully evaluated during the planning stages of wind energy projects.
As the world moves towards more sustainable energy solutions, the role of wind energy continues to grow. It not only helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also supports energy security by diversifying the energy mix. Understanding the fundamentals of wind energy lays the groundwork for appreciating its potential and addressing the challenges associated with its implementation.
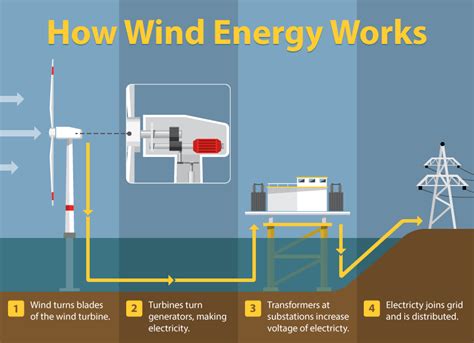
How Wind Turbines Convert Wind Energy Into Electricity
Understanding how wind turbines convert wind energy into electricity is crucial for grasping the mechanics behind renewable energy. Wind turbines operate on a simple yet effective principle: they transform kinetic energy from the wind into electrical energy through a series of steps.
Here’s a breakdown of the process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Wind Capture | The blades of the turbine catch the wind, causing them to turn. The design of the blades is optimized for capturing maximum wind energy. |
| 2. Rotor Movement | The turning blades spin the rotor connected to the generator. This is where the mechanical energy is created. |
| 3. Electricity Generation | As the rotor spins, it activates the generator, which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. |
| 4. Power Transmission | The generated electricity is then transferred through power lines for use in homes, industries, and grid systems. |
This process exemplifies how effectively wind energy can be used to produce clean, sustainable power. With technology advancing rapidly, the efficiency of these systems continues to improve, further enhancing their viability as a renewable energy source.
The Role of Wind Speed in Energy Generation
The generation of wind energy is highly dependent on wind speed; it is one of the most crucial factors influencing the efficacy and efficiency of wind turbines. When the wind speed reaches a specific threshold, known as the cut-in speed, turbines begin to generate electricity. Typically, this speed ranges from 3 to 6 meters per second (m/s). However, the amount of energy harnessed increases significantly as wind speeds rise.
Each turbine has a rated wind speed, which is the wind speed at which it generates its maximum output. This speed is usually around 12 to 15 m/s. As the wind speed increases beyond this point, the turbines have mechanisms to limit the power output to prevent damage, ensuring longevity and safety.
Here’s a breakdown of how different wind speed ranges affect energy output:
| Wind Speed (m/s) | Performance |
|---|---|
| 3 – 6 | Cut-in speed; turbines start generating power. |
| 12 – 15 | Rated speed; turbines produce maximum output. |
| Over 25 | Turbines may shut down to prevent damage. |
In addition to the cut-in and rated wind speeds, the variability of wind speed is also essential. Regions with consistent wind patterns can enhance the reliability of wind energy production, making them ideal for wind farm installations. Understanding these dynamics allows energy planners and engineers to strategically position turbines and optimize energy output.
Harnessing the full potential of wind energy requires careful consideration of wind patterns and speeds, enabling sustainable energy solutions to meet growing demands.
Benefits of Harnessing Wind Energy for Sustainable Power
Wind energy offers numerous advantages as a source of clean and renewable power. By tapping into the natural energy produced by wind, we can reap significant benefits for both the environment and the economy. Here are some of the key benefits of harnessing wind energy:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Renewable Resource | Wind energy is a limitless resource, unlike fossil fuels, which can be depleted. |
| Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Utilizing wind energy significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner atmosphere. |
| Economic Growth | The wind energy sector creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, boosting local economies. |
| Energy Independence | Investing in wind energy can help reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels, enhancing national energy security. |
| Low Operating Costs | Once established, wind farms have low operational and maintenance costs compared to traditional energy sources. |
The adoption of wind energy as a primary power source brings significant benefits that align with sustainable development goals. By embracing this renewable form of energy, we not only foster economic growth but also play a crucial role in combating climate change.
Challenges in Wind Energy Production and Solutions
While wind energy is a promising and sustainable power source, it does come with its own set of challenges. Addressing these obstacles is crucial to optimizing the efficiency and effectiveness of wind energy production. Here, we explore some of the key challenges and potential solutions.
1. Intermittency of Wind
Wind energy generation is highly dependent on wind speed and weather conditions. This intermittency can lead to fluctuations in power supply, making it difficult to rely solely on wind energy to meet energy demands.
Solutions: To counter this challenge, energy storage technologies such as batteries can be employed to store excess energy generated during high wind periods. Additionally, integrating wind energy with other renewable sources can provide a more stable energy supply.
2. Location Limitations
Effective wind energy production requires specific geographical conditions such as open spaces and consistent wind patterns. This can limit where wind farms can be built.
Solutions: Advances in technology, such as floating wind turbines, can expand the range of viable locations by allowing for installations farther offshore where winds tend to be stronger and more consistent.
3. Environmental and Social Concerns
The development of wind farms can lead to concerns regarding bird and bat mortality, noise, and visual impact on landscapes. Communities may also resist changes in their environment.
Solutions: Thorough environmental impact assessments and the implementation of technology designed to mitigate wildlife impacts can help address these concerns. Engaging with local communities during the planning phase can also foster acceptance and minimize opposition.
4. High Initial Costs
The upfront capital required for building wind farms can be significant, which may deter investors and project developers.
Solutions: Government incentives, subsidies, and tax credits can make investments more attractive. Furthermore, as technology advances, the costs associated with wind energy production are continually decreasing, making it a more viable option over time.
5. Maintenance and Operational Challenges
Wind turbines require regular maintenance, and unexpected repairs can lead to downtime, which affects power generation.
Solutions: Predictive maintenance utilizing data analytics and machine learning can improve operational efficiency and reduce unplanned outages by anticipating and addressing maintenance needs before they lead to turbine failure.
While there are several challenges associated with wind energy production, a combination of innovative solutions and advancements in technology can help overcome these hurdles, paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Global Adoption of Wind Energy: Trends and Statistics
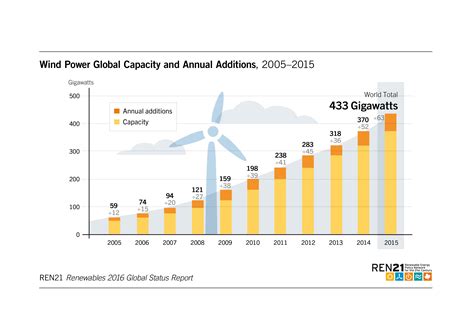
The adoption of wind energy has seen remarkable growth over the past few decades as countries shift towards sustainable energy sources. According to the Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), the global installed capacity of wind energy has surpassed 900 gigawatts (GW) as of 2023, reflecting a substantial increase from just 50 GW in the year 2000.
Several key trends are shaping the future of wind energy adoption globally:
| Year | Global Installed Capacity (GW) | Annual Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 50 | – |
| 2010 | 197 | 24.6 |
| 2020 | 743 | 15.4 |
| 2023 | 900+ | approximately 10 |
One of the most significant factors contributing to the growth of wind energy is the decreasing cost of wind power generation. Recent studies have indicated that the cost of onshore wind energy has fallen by nearly 50% since 2010. This decline in costs has made wind energy a competitive alternative to fossil fuels in many regions.
The geographic distribution of wind energy installations has also evolved. Countries such as China, the United States, and Germany continue to lead in installed capacity, but emerging markets in India, Brazil, and South Africa are rapidly increasing their wind energy output.
As governments worldwide set ambitious renewable energy targets and commit to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the outlook for wind energy remains strong. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that wind power could contribute significantly to global electricity generation by 2030, potentially supplying over 20% of global energy needs.
The global adoption of wind energy is on a remarkable trajectory, driven by technological advances, economic viability, and regulatory support. As countries increasingly recognize the importance of sustainable energy, the role of wind energy will undoubtedly continue to expand in the multi-faceted energy landscape.
The Future of Wind Energy: Innovations and Developments
The future of wind energy: is poised for transformative changes driven by ongoing innovations and developments in technology, infrastructure, and policies. As the world continues to seek sustainable energy sources, the wind energy sector is expected to play an increasingly pivotal role in reducing carbon emissions and enhancing energy independence.
Some key areas of focus for the future of wind energy: include:
| Innovation | Description |
|---|---|
| Floating Wind Turbines | These offshore wind turbines are anchored to the seabed, allowing for deeper water installations where wind resources are more abundant. |
| Smart Grid Technology | Integration of advanced grid technologies to optimize wind energy distribution and manage variable supply more effectively. |
| Energy Storage Solutions | Improved battery and other storage technologies to store excess energy generated during peak wind conditions for later use. |
| Advanced Materials | Development of lighter, more durable materials to enhance turbine efficiency and lifespan, with a focus on reducing maintenance costs. |
Additionally, governmental policies and incentives are expected to play a significant role in advancing research and development in the wind energy: sector. Over the next decade, we can anticipate a surge in public and private investments aimed at expanding wind farms, enhancing grid interconnections, and fostering community-based wind energy initiatives.
As technological innovations continue to reshape the landscape, the future of wind energy: looks bright, promising a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Wind energy is the conversion of wind motion into usable electrical or thermal energy through the use of wind turbines.Wind turbines generate electricity by converting the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy, which then turns a generator to produce electricity.The main components of a wind turbine include the rotor blades, hub, tower, nacelle (which houses the generator), and the control system.The efficiency of wind energy depends on factors such as wind speed, turbine design, rotor size, and the height of the turbine above the ground.The advantages of wind energy include its renewability, low operational costs, minimal environmental impact, and its ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.Challenges include variability in wind strength, potential impacts on wildlife, noise concerns, and the need for substantial initial investment.Wind energy is often seen as one of the most efficient renewable sources compared to solar and hydro, due to its lower operational costs and higher energy generation potential in suitable locations.