Introduction
- Overview of AI and its role in green energy.
- The importance of sustainable energy solutions.
The Role of AI in Optimizing Renewable Energy Systems
- AI’s role in improving the efficiency of solar, wind, and other renewable energy systems.
- Example: Google DeepMind’s contribution to wind energy prediction.
Smart Grids and AI: Enhancing Energy Distribution
- How AI-powered smart grids work.
- Real-time data and grid management.
- Example: Power outage management using AI.
AI-Driven Energy Storage Solutions
- AI’s role in managing and optimizing energy storage systems.
- Example: Tesla’s AI-driven Powerwall.
AI-Powered Energy Management in Buildings
- AI applications in reducing energy consumption in residential and commercial buildings.
- Example: Google’s Nest Thermostat.
AI in Energy Transition and Policy
- The role of AI in supporting government policies and global energy transitions.
- Example: AI’s impact on EU climate policies.
The Future of AI and Green Energy
- Predictions for future AI applications in green energy.
- Decentralized energy systems and blockchain technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- How does AI improve renewable energy efficiency?
- What is a smart grid and how does AI support it?
- How does AI help in energy storage?
- Can AI contribute to reducing energy consumption in buildings?
- What is the role of AI in the global energy transition?
Conclusion
- Summary of AI’s growing influence in driving sustainability.
- The future outlook for AI and renewable energy integration.
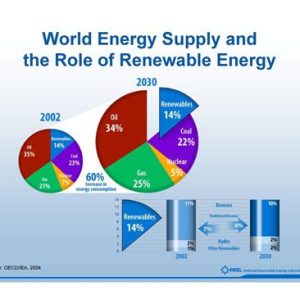
The convergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and green energy is shaping the future of global sustainability efforts. With the planet facing unprecedented environmental challenges due to climate change, energy crises, and pollution, it has become increasingly crucial to explore efficient and sustainable energy solutions. In this context, AI is emerging as a powerful tool that optimizes energy use, improves grid systems, and fosters the growth of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower.
This article will delve into the numerous ways AI is transforming the green energy landscape, the technologies driving this transformation, and how these innovations are set to revolutionize the way we produce and consume energy.

1. The Role of AI in Optimizing Renewable Energy Systems
AI’s role in enhancing the efficiency of renewable energy systems cannot be overstated. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are inherently variable and weather-dependent. This variability poses challenges in terms of grid stability and consistent energy supply. AI algorithms can predict energy output from renewable sources by analyzing weather patterns, past energy production data, and other critical factors.
For instance, AI-powered forecasting models are capable of predicting the amount of solar or wind energy that will be generated over a certain period. By using this data, energy providers can efficiently distribute energy, manage storage solutions, and adjust the energy supply in real-time. These AI systems are especially useful in balancing supply and demand, helping to reduce wastage and ensuring that renewable energy is used to its full potential.
Example: Google’s DeepMind and the Wind Energy Forecasting System
One practical example of this is Google’s DeepMind project, which has applied AI to improve the efficiency of wind farms. By using machine learning algorithms, DeepMind was able to predict wind output 36 hours in advance, allowing grid operators to plan accordingly. This resulted in a 20% increase in the value of wind energy production.
2. Smart Grids and AI: Enhancing Energy Distribution
A smart grid is an advanced electrical grid that uses digital communications technology to detect and react to local changes in usage. The combination of AI and smart grids plays a pivotal role in managing energy distribution more effectively.
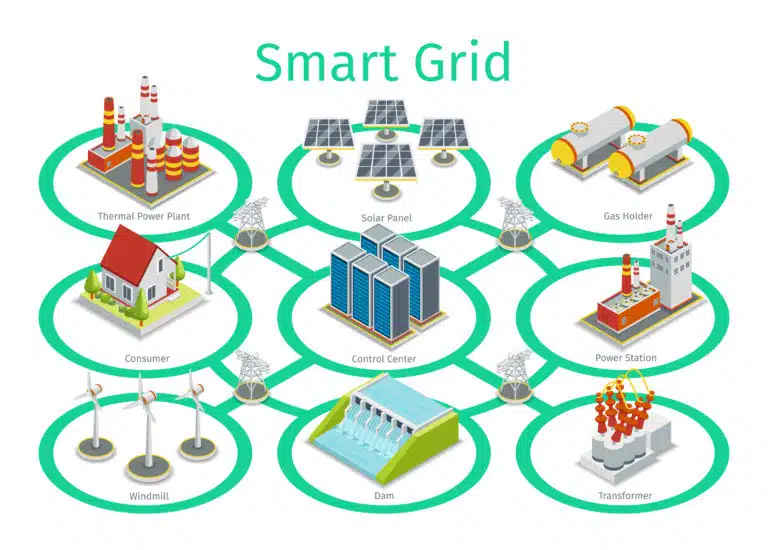
Traditional grids rely on centralized power plants and unidirectional power flows. However, as renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines become more decentralized, the complexity of managing power distribution increases. AI optimizes this process by analyzing real-time data and automating decision-making to adjust energy flows, thus maintaining grid stability.
Through the integration of AI, smart grids can:
- Identify peak demand periods and adjust power supply.
- Predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime.
- Coordinate energy storage systems, such as batteries, to release stored energy when renewable production is low.
- Reduce transmission losses, ensuring more efficient use of energy.
Example: AI in Power Outage Management
AI is also helping in power outage management. By analyzing data from IoT sensors placed across the grid, AI can pinpoint faults or anomalies and suggest corrective actions. This minimizes downtime, improving the reliability of renewable energy systems.
3. AI-Driven Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage plays a crucial role in the transition to green energy. One of the biggest challenges facing renewable energy sources like wind and solar is their intermittent nature. However, AI-driven energy storage systems can balance supply and demand by storing excess energy when production is high and releasing it when production is low.
For example, smart batteries equipped with AI can store solar energy generated during the day for use during the night. AI also optimizes the charge and discharge cycles of batteries, ensuring the most efficient use of energy resources.

Example: Tesla’s AI-Driven Powerwall
Tesla’s Powerwall system, for example, is a smart home battery that stores energy generated from solar panels or the grid. Through machine learning algorithms, Powerwall learns about a home’s energy needs and adapts its storage and usage patterns to maximize efficiency.
4. AI-Powered Energy Management in Buildings
Buildings are responsible for a significant portion of global energy consumption, particularly in cities. AI-driven energy management systems are becoming increasingly popular for reducing energy waste in both residential and commercial buildings.
These systems rely on machine learning algorithms that learn the habits of occupants, adjusting heating, lighting, and cooling systems accordingly. Smart thermostats, for example, can predict when a room will be occupied and adjust the temperature in advance, resulting in significant energy savings.
Example: Google’s Nest Thermostat
Google’s Nest Thermostat is an AI-powered device that learns a user’s behavior over time. It adjusts the temperature of a home based on when residents are likely to be home or away, thereby reducing unnecessary energy consumption.
5. AI in Energy Transition and Policy
The global push toward net-zero emissions has spurred governments and corporations to adopt cleaner energy solutions. AI plays an important role in policy-making and the energy transition by analyzing vast datasets related to energy consumption, environmental impact, and economic factors.
AI can simulate various energy scenarios, helping policymakers understand the potential outcomes of their decisions. For instance, AI can model how quickly an economy can transition to renewable energy sources based on current infrastructure and investment trends.
Example: AI Supporting Climate Policy in the EU
In Europe, AI is being used to support climate policy initiatives by forecasting the impacts of various energy policies on emissions. This helps governments make data-driven decisions and allocate resources more efficiently.
6. The Future of AI and Green Energy
As AI technologies continue to advance, their application in green energy will become even more critical. In the future, we can expect to see:
- AI-powered microgrids, where communities generate, store, and manage their own renewable energy.
- Decentralized energy systems, where individuals and businesses have more control over their energy consumption.
- Blockchain-enabled energy trading platforms, allowing consumers to buy and sell renewable energy in real-time.
The integration of AI and renewable energy not only promises to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels but also to enhance energy efficiency and lower carbon emissions globally. The coming years will see further AI innovations that will push the boundaries of what’s possible in sustainable energy.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How does AI improve renewable energy efficiency?
AI enhances renewable energy efficiency by predicting weather patterns and energy output, optimizing grid stability, and balancing energy supply and demand in real-time.
2. What is a smart grid and how does AI support it?
A smart grid is an advanced power grid system that uses digital communication to manage electricity flows. AI supports smart grids by automating energy distribution, predicting equipment failures, and reducing transmission losses.
3. How does AI help in energy storage?
AI-driven energy storage systems balance energy supply and demand by optimizing the charge and discharge cycles of batteries, allowing for better use of renewable energy.
4. Can AI contribute to reducing energy consumption in buildings?
Yes, AI-powered energy management systems can learn usage patterns in buildings and adjust heating, cooling, and lighting systems to reduce energy waste.
5. What is the role of AI in the global energy transition?
AI assists in the energy transition by analyzing large datasets, supporting policy decisions, and simulating various energy scenarios to optimize the shift to renewable energy.
Conclusion
The intersection of AI and green energy represents a critical juncture in the fight against climate change. AI’s ability to optimize energy systems, predict renewable energy output, and manage smart grids makes it a valuable tool in the global transition to cleaner energy. As AI technologies continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly central role in creating a more sustainable future, helping both governments and individuals reduce their carbon footprint while improving energy efficiency.
Through AI-driven innovations, we are on the verge of a cleaner, more efficient energy system that will define the future of sustainability. The challenge now lies in fully integrating these technologies and ensuring they are accessible to all.