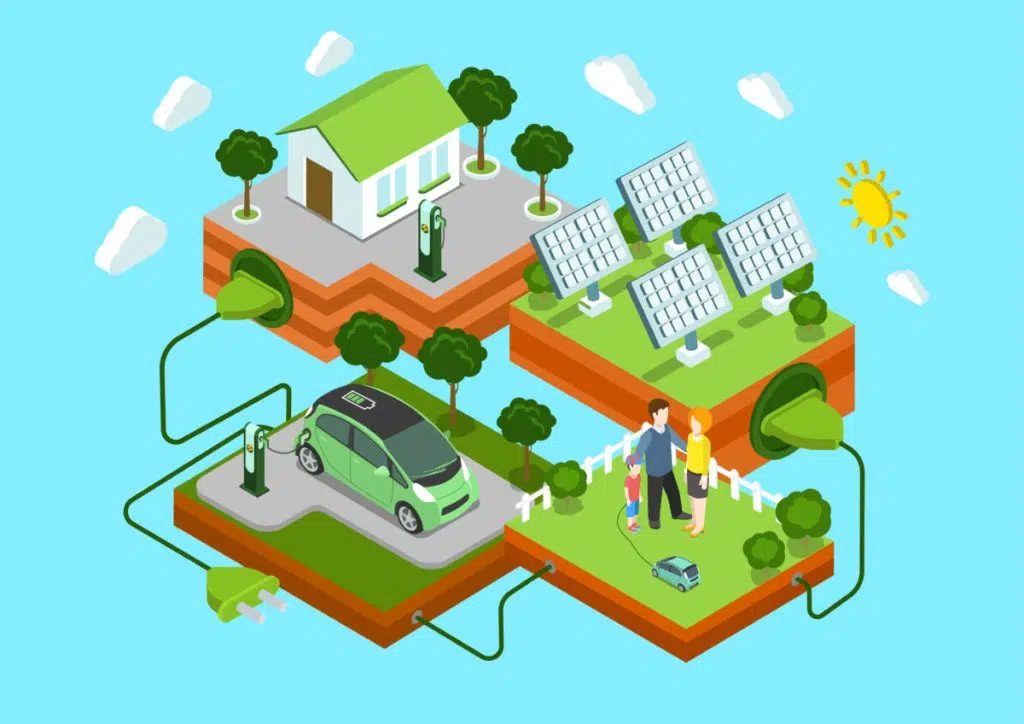
Introduction
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is soaring worldwide, fueled by the need to reduce carbon emissions and the availability of advanced renewable energy technologies. As the demand for sustainable transportation grows, integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into the EV ecosystem becomes increasingly crucial. This article explores the relationship between EVs and renewable energy, focusing on the key technologies driving this integration, challenges, and the future potential of a fully green transportation system.
1. The Rise of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
A. Growth in Global EV Adoption
Over the past decade, electric vehicles have shifted from being a niche technology to becoming a mainstream transportation solution. In 2024, EV sales are expected to reach record highs, supported by:
- Government incentives (e.g., tax credits and rebates)
- Technological advancements in battery storage
- A growing awareness of the environmental benefits
Companies like Tesla, Volkswagen, and Nissan have made significant strides in producing affordable and efficient EV models, further boosting adoption rates.
B. Environmental Benefits of EVs
EVs offer substantial environmental advantages over internal combustion engine vehicles, including:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
- Lower levels of air pollution in cities
- The ability to be powered by renewable energy sources

2. Renewable Energy and EV Integration
A. Solar-Powered EV Charging Stations
A significant step towards fully sustainable EVs is the development of solar-powered charging stations. These stations harness solar energy to charge EV batteries, eliminating the reliance on grid power, which may still come from fossil fuels.
- Tesla’s Solar Supercharger Stations: Tesla has pioneered solar-powered supercharger networks, offering renewable energy to its users.
- Public and Private Charging Networks: Many companies are investing in the development of solar-powered EV chargers for public infrastructure and private homes, making clean energy accessible for EV owners.
B. Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology
Another groundbreaking innovation is Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology, which allows EVs to return energy to the grid. This creates a two-way flow of electricity, enabling vehicles to store excess renewable energy during off-peak hours and send it back to the grid when needed.
- Nissan’s LEAF: One of the first commercially available V2G-compatible vehicles, the Nissan LEAF can feed energy back into the grid, offering greater energy flexibility and reducing dependence on traditional power plants.
- Energy Grid Balancing: V2G can play a crucial role in balancing the energy grid, particularly when integrated with renewable energy sources like wind and solar, which have variable generation rates.

3. Battery Storage: A Key Enabler
A. The Role of Lithium-Ion Batteries
The efficiency of EVs largely depends on the development of lithium-ion batteries, which provide higher energy density and longer driving ranges. These batteries also support energy storage from renewable sources, further integrating EVs into a sustainable energy system.
B. Second-Life EV Batteries
Once EV batteries reach the end of their life for vehicle use, they can be repurposed for energy storage systems, extending their lifespan and supporting the grid storage of renewable energy.
- Tesla Powerwall: Tesla’s Powerwall is an example of how used EV batteries can be reconditioned and used for home energy storage, offering homeowners the ability to store solar energy and reduce reliance on the traditional grid.
4. Challenges in EV and Renewable Energy Integration
A. Infrastructure Development
One of the primary challenges in EV adoption is the lack of sufficient charging infrastructure, especially in rural areas. The integration of renewable energy into this infrastructure adds complexity, as it requires the development of solar or wind-powered charging stations.
- Charging Network Expansion: Companies and governments are investing in expanding the network of renewable-powered charging stations to support a wider EV user base.
B. Renewable Energy Variability
The intermittent nature of solar and wind power poses challenges for providing consistent energy for EVs. Energy storage solutions like batteries and smart grid technology are essential to overcome this issue, ensuring a reliable supply of clean energy for EV charging.
5. The Future of EV and Renewable Energy Integration
A. Smart Charging Systems
The future of EV charging lies in the development of smart charging systems that optimize charging times based on renewable energy availability. By using AI and machine learning, smart chargers can determine when to charge vehicles based on the cheapest and cleanest energy available, ensuring efficient and environmentally friendly charging.
B. The Role of Policy and Government Support
Governments worldwide are providing strong policy frameworks to support the integration of EVs with renewable energy. Policies that encourage the development of green energy infrastructure, such as subsidies for solar-powered chargers and tax incentives for V2G-compatible vehicles, are essential for driving this transition.
C. A Vision for a Sustainable Transportation System
In the long term, the combination of renewable energy and electric vehicles could lead to a completely carbon-neutral transportation system. As more countries commit to phasing out internal combustion engines, renewable energy will play a pivotal role in powering the next generation of clean vehicles, making sustainable transportation a reality.
Conclusion
The integration of electric vehicles and renewable energy is crucial for achieving a sustainable future. With advancements in technologies like V2G, solar-powered charging, and smart grids, the possibility of a fully green transportation system is becoming more realistic. However, challenges such as infrastructure development and energy variability must be addressed to fully realize the potential of this green revolution.
FAQ: Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy Integration
- How do electric vehicles contribute to reducing carbon emissions?
- EVs eliminate direct emissions by not burning fossil fuels. When charged using renewable energy sources like solar or wind, they significantly reduce overall carbon footprints, offering a cleaner alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles.
- What is Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology?
- V2G technology allows electric vehicles to return stored energy to the grid, helping balance electricity supply and demand. It enables EVs to store renewable energy and contribute back to the grid during peak demand periods.
- Can electric vehicles be powered directly by renewable energy?
- Yes, solar-powered EV charging stations are being developed to provide clean, renewable energy for EVs. Additionally, homeowners with solar panels can use solar energy to charge their vehicles.
- What are the challenges in integrating EVs with renewable energy?
- The primary challenges include the lack of infrastructure for renewable-powered charging stations and the variability of renewable energy sources like wind and solar. However, advancements in energy storage are helping address these challenges.
- What is the future of electric vehicles and renewable energy integration?
- The future includes smart charging systems, expanded solar-powered charging networks, and policy support for renewable energy infrastructure. These innovations will help create a fully sustainable transportation system, significantly reducing carbon emissions.