Explore the benefits, practical steps, and cost considerations of transitioning your home to renewable energy, along with tips for monitoring your system.In an era where sustainability is becoming increasingly vital, transitioning your home to 100% renewable energy is not just a trend—it’s a necessity. As homeowners seek to reduce their carbon footprint and embrace eco-friendly living, this guide will walk you through the essential steps of making the switch to clean energy. From evaluating your current energy needs to exploring the various renewable sources available, we aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary for a successful transition. You’ll learn about the numerous benefits of renewable energy, practical implementation strategies, and considerations for monitoring and optimizing your new system. Join us as we embark on this journey towards a greener, more sustainable home, ensuring both environmental responsibility and potential cost savings for years to come.
Understanding The Benefits Of Transitioning To Renewable Energy
Transitioning your home to renewable energy offers a multitude of advantages that extend beyond just environmental benefits. Here are some key reasons to consider this significant change:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Utilizing renewable energy reduces greenhouse gas emissions, combating climate change and preserving natural resources. |
| Energy Independence | Generating your own energy means less reliance on fossil fuels and external power sources, enhancing energy security. |
| Long-term Financial Savings | After the initial setup costs, renewable energy systems can lead to significantly lower energy bills and potential returns through incentives. |
| Increased Property Value | Homes equipped with renewable energy systems can appeal to eco-conscious buyers and have been shown to increase in value. |
| Technological Advancements | Embracing renewable energy often leads to access to innovative technologies and energy management solutions. |
| Job Creation | The shift towards renewable energy supports job growth in new industries focused on clean energy technologies and infrastructure. |
Opting to transition to renewable energy not only benefits your household but also contributes to a more sustainable future. The overall impact on the environment, economy, and community makes this transition a worthwhile investment for any homeowner.
Evaluating Your Home’s Energy Needs For A Smooth Transition
Before embarking on the journey to transition to renewable energy, it is essential to conduct a thorough evaluation of your home’s energy needs. This step ensures that your system is appropriately sized and can meet your household’s energy requirements, ultimately leading to a more successful transition.
Here are some key factors to consider:
- Energy Consumption Analysis: Start by reviewing your electricity bills over the past year. This will help you gauge your average monthly and seasonal energy usage. Take note of any fluctuating consumption patterns that may arise due to seasonal activities.
- Energy Audit: Conducting a home energy audit can pinpoint areas where your home might be wasting energy. This may include checking for inefficient appliances, poor insulation, or air leaks around doors and windows.
- Current Energy Sources: Identify your current energy sources and their contributions to your overall consumption. Understanding where your energy comes from will help you strategize which renewable options are best suited for your needs.
- Future Energy Needs: Consider any planned changes in your life that may affect energy use. For instance, if you plan to expand your home, purchase new appliances, or acquire electric vehicles, factor these potential increases into your energy needs assessment.
- System Performance Expectations: Research the performance and efficiency of renewable energy systems you are considering. Understanding how much energy you can expect from solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable sources will help you plan accordingly and ensure a smooth integration into your home.
By carefully evaluating your home’s energy needs, you can make informed decisions about how to effectively transition to renewable energy. This preparation not only streamlines the installation process but also maximizes the benefits of your new renewable energy system.
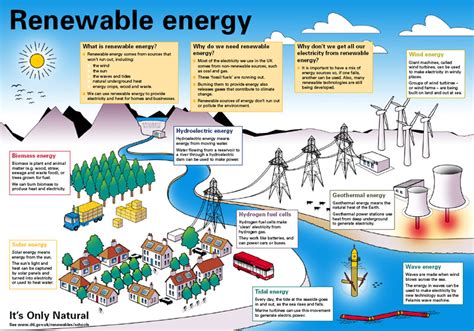
Exploring Available Renewable Energy Sources For Homes
When considering a transition to renewable energy, it is essential to explore the various sources available that can be harnessed for residential use. Each option comes with its own benefits and suitability depending on your location, home structure, and energy needs. Here are some of the most common renewable energy sources for homes:
- Solar Power: Solar panels are one of the most popular forms of renewable energy for homes. They convert sunlight into electricity, making them ideal for areas with ample sunlight. Installing solar panels can significantly reduce your electricity bills and carbon footprint.
- Wind Energy: If you live in a region with consistent winds, small wind turbines can be an effective option for generating electricity. Homeowners can install these turbines to harness wind energy, especially in rural settings where space and wind flow are abundant.
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal systems tap into the earth’s internal heat for heating and cooling. This renewable energy source can be an excellent option for homes in geographical areas rich with geothermal resources. Geothermal heat pumps can provide a reliable and efficient heating solution.
- Biomass Energy: Biomass energy involves using organic materials, such as wood, crop waste, or animal manure, to produce heat or electricity. This source can often utilize waste products, making it an efficient and environmentally friendly choice for some homeowners.
- Hydropower: For homes near rivers or streams, small-scale hydroelectric systems can provide a steady source of energy. This option generally requires a more significant initial investment and is suited for properties with adequate water flow.
When considering a transition to renewable energy, it is important to assess which of these sources aligns best with your home’s location, budget, and energy requirements. Combining multiple renewable sources can also maximize efficiency and reliability.
Practical Steps To Transition A Home To Renewable Energy
Transitioning your home to 100% renewable energy involves several practical steps. Here’s a structured approach to make the process seamless:
1. Conduct an Energy Audit: Start by assessing your current energy usage. An energy audit will help identify areas where you can reduce consumption and integrate renewable sources efficiently.
2. Choose Your Renewable Energy Type: Decide on which renewable energy sources best fit your home. The most common options are solar, wind, and geothermal energy. Each comes with its own set of requirements and benefits.
3. Install Solar Panels: If you choose solar energy, consider the size and orientation of your roof. Install solar panels that align with your energy needs and local regulations.
4. Consider Wind Turbines: For homes in areas with consistent wind, small wind turbines may be an option. Check local zoning laws and potential restrictions that might apply.
5. Implement Energy Storage Solutions: Invest in battery storage systems to store excess energy generated from renewable sources. This will ensure you have power available even when production is low.
6. Upgrade Your Appliances: Replace old appliances with energy-efficient models designed to work effectively with renewable energy systems. Look for the ENERGY STAR label when shopping.
7. Enhance Home Insulation: Proper insulation minimizes energy loss and optimizes the efficiency of your renewable energy system. Consider upgrading windows and sealing gaps in your home’s structure.
8. Use Smart Technologies: Implement smart thermostats and home energy management systems to optimize energy usage actively. These technologies can help you monitor and adjust your energy consumption in real time.
9. Connect With Local Energy Providers: Work with your local utility company to understand net metering policies. This allows you to sell excess energy back to the grid, maximizing your investment.
10. Form a Community Network: Engage with neighbors and local initiatives focused on renewable energy. Collaborative efforts can yield better pricing on installations and a stronger push for clean energy in your community.
By following these practical steps, you will efficiently transition your home to renewable energy, paving the way for a sustainable and eco-friendly future.
Cost Considerations When Transitioning To Renewable Energy

Transitioning to renewable energy can lead to significant long-term savings, but it’s important to first assess the initial costs involved. Here are some key financial factors to consider:
The primary costs associated with transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, or geothermal include:
- Initial Installation Costs: The price of purchasing and installing renewable energy systems can vary widely. For instance, solar panels may cost between $15,000 to $30,000, depending on the system size and type.
- Financing Options: Many homeowners opt for financing solutions like solar loans or leases, which can spread the cost over time. Examine interest rates and loan periods to find the most advantageous option for your situation.
- Incentives and Rebates: Research available local, state, and federal incentives. These can significantly reduce costs, sometimes covering up to 30% of the installation price in tax credits.
- Maintenance Costs: Although renewable energy systems generally require less maintenance than traditional energy sources, regular upkeep is still necessary. Budget for periodic inspections or repairs to keep the system functioning efficiently.
- Insurance Costs: It may be worth adjusting your home insurance to cover renewable energy equipment against damage or loss. Discuss options with your insurance provider to ensure you’re fully covered.
- Utility Savings: Consider the decrease in your monthly utility bills. Transitioning to renewable energy could mean substantial savings over time, effectively offsetting upfront costs.
While the upfront investments for transitioning to renewable energy can be substantial, evaluating the various financial aspects can help you make informed decisions. Consider both immediate expenses and long-term savings to effectively assess the value of making the switch.
How To Monitor And Optimize Your Renewable Energy System
Monitoring and optimizing your renewable energy system is crucial to ensure that you maximize efficiency and benefits from your investment. Here are several strategies to effectively manage your system:
By taking these steps, you can actively transition to renewable energy in a way that ensures sustainable performance and cost savings for your home.
Frequently Asked Questions
The first steps include assessing your current energy consumption, determining the feasibility of renewable energy options like solar or wind, and setting a budget for the transition.Common renewable energy sources for homes include solar panels, wind turbines, geothermal systems, and biomass.You can assess your energy needs by reviewing past energy bills, calculating the average monthly usage in kilowatt-hours (kWh), and considering any future changes in energy consumption.Net metering allows homeowners with renewable energy systems to sell excess energy back to the grid, effectively reducing their energy bills and providing a financial incentive for using renewable energy.Many governments offer tax credits, rebates, and financing options to encourage the adoption of renewable energy, making it more affordable for homeowners.Improving energy efficiency through upgrades like insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and smart thermostats can reduce energy demands, making the transition to renewable energy more effective and economical.Maintenance requirements vary by technology, but generally, solar panels require occasional cleaning, wind turbines need inspections for mechanical issues, and geothermal systems may need periodic checks of the heat pump.