Explore the historical growth, benefits, challenges, and future of U.S. renewable energy, highlighting sources, economic impact, and technological innovations.As the world shifts towards a more sustainable future, the importance of renewable energy has never been more pronounced. The U.S. Renewable Energy Factsheet serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the evolution, current state, and future of renewable energy in the United States. From its historical roots to the innovative technologies propelling its growth, this factsheet delves into key renewable sources, their environmental benefits, and the economic impact in terms of job creation. While challenges remain, the outlook for U.S. renewable energy development is promising. Join us as we explore the critical facets of this dynamic sector, highlighting not only its achievements but also the road ahead in our collective pursuit of cleaner, greener energy solutions.
The Rise Of U.S. Renewable Energy: A Historical Overview
The journey of U.S. renewable energy has been marked by significant milestones that reflect the country’s evolving approach to energy production. Beginning in the late 19th century, the U.S. saw the initial harnessing of renewable resources, particularly hydropower. The early 1900s brought the establishment of hydroelectric power plants, which laid the groundwork for future renewable energy developments.
With the advent of the 1970s oil crisis, a pressing need for energy diversification emerged. This decade marked a turning point, leading to increased government investment and research into alternative energy sources. The creation of the Department of Energy in 1977 highlighted the commitment to energy independence, especially through renewable avenues.
The 1990s signified another leap forward with the introduction of the Energy Policy Act of 1992, which promoted renewable energy technologies. This act provided incentives for the development of wind and solar energy, contributing to a gradual rise in the adoption of these resources across the United States.
The new millennium saw a burgeoning interest in addressing climate change, further propelling the growth of U.S. renewable energy. By the mid-2000s, wind and solar energy began to gain considerable traction, supported by state-level policies and federal tax incentives. The Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS), implemented by numerous states, required utilities to source a percentage of their energy from renewable sources, significantly boosting the market.
As technology advanced, the cost of renewable energy systems declined, making them more accessible. By 2010, solar photovoltaic (PV) systems started to become commonplace, while wind energy production surged across the plains of the Midwest.
In recent years, the U.S. has witnessed groundbreaking achievements in renewable energy capacity. The growth trend continued, with the U.S. becoming a global leader in both wind turbine production and solar installations. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), total renewable energy consumption has more than doubled from 2000 to 2020.
The commitment to renewable energy is further evidenced by various state initiatives and the Green New Deal proposals, emphasizing a sustainable and equitable energy future. The historical trajectory of U.S. renewable energy reflects a paradigm shift towards a more sustainable energy landscape, underscoring the importance of policy, innovation, and public awareness in driving this transition.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1882 | First commercial hydroelectric power plant opens in Appleton, Wisconsin. |
| 1977 | Creation of the Department of Energy to promote energy independence. |
| 1992 | Energy Policy Act established incentives for renewable technology. |
| 2005 | Renewable Portfolio Standards implemented in many states. |
| 2020 | Renewable energy consumption surpasses 20% of total U.S. energy consumption. |
Key Sources Of U.S. Renewable Energy And Their Growth
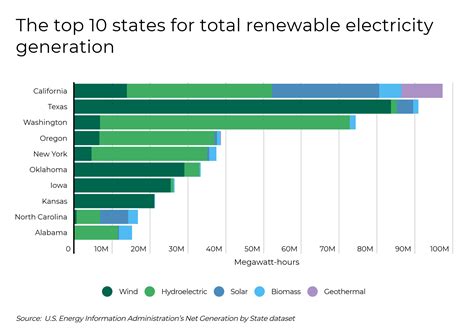
The U.S. Renewable energy landscape has experienced significant transformation over the past few decades, characterized by the growth of various energy sources. Below, we explore the key sources of renewable energy in the United States and their remarkable expansion.
- Solar Energy: Solar power is one of the fastest-growing sources of U.S. Renewable energy. The deployment of solar panels has increased tremendously, with residential and utility-scale installations making solar a key player in America’s energy mix. According to reports, solar energy accounted for approximately 3% of the total electricity generated in the U.S. in 2020, a figure that is projected to rise significantly in coming years.
- Wind Energy: Wind energy has also seen substantial growth, especially in the Midwest and Texas. By 2020, wind was generating about 20% of the total renewable energy output in the U.S. With advancements in turbine technology and supportive policies, wind energy is poised for continued expansion, particularly offshore wind projects.
- Hydropower: While hydropower has been a traditional source of renewable energy in the U.S., its growth has stabilized in recent years. As of 2020, hydropower constituted approximately 40% of renewable energy generation. Most existing facilities are aging, prompting a shift towards modernization and efficiency rather than new large-scale projects.
- Biomass: Biomass energy, derived from organic materials such as wood, agricultural crops, and waste, plays a crucial role in the renewable energy sector. It represents around 5% of the U.S. Renewable energy mix, and innovations in conversion technology are helping to enhance its viability as a carbon-neutral energy source.
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy harnesses heat from the Earth’s interior and remains a reliable, low-emission source of power. Although its share of total energy production is small, around 0.4% in 2020, the potential for growth in geothermal energy is significant, particularly in areas with abundant geothermal resources.
The key sources of U.S. Renewable energy — solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, and geothermal — each contribute to the nation’s efforts to transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. As technology advances and investments continue, the growth trajectory of these renewable energy sources is expected to remain positive, marking an essential step towards a sustainable economy.
Benefits Of U.S. Renewable Energy For The Environment
The shift towards U.S. Renewable energy sources brings a multitude of benefits for the environment. Here are some of the most significant advantages:
- Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions: One of the primary benefits of renewable energy is its potential to drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike fossil fuels, which release carbon dioxide and other harmful gases upon combustion, renewable sources like wind, solar, and hydropower produce little to no emissions during operation.
- Improved Air Quality: Transitioning to renewable energy contributes to cleaner air. Reduced dependence on coal and oil leads to a decrease in air pollutants, which can improve overall public health and reduce healthcare costs associated with air pollution-related illnesses.
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Renewable energy technologies utilize resources that are abundant and locally available, such as sunlight, wind, and water, reducing the need for resource extraction that can harm ecosystems.
- Protection of Biodiversity: By investing in U.S. Renewable energy, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change, which threatens biodiversity. Cleaner energy can help protect habitats and the species that depend on them.
- Mitigation of Climate Change: Increased use of renewable energy contributes to a significant reduction in global warming potential, aiding in the fight against climate change. This can have long-term positive effects on weather patterns, sea levels, and the overall health of the planet.
- Low Water Usage: Many renewable energy systems, particularly solar and wind, require significantly less water compared to fossil fuel extraction and processing. This helps alleviate pressure on local water resources, especially in arid regions.
Overall, the transition to U.S. Renewable energy sources leads to a healthier, more sustainable environment for current and future generations.
Economic Impact: Job Creation In U.S. Renewable Energy Sector
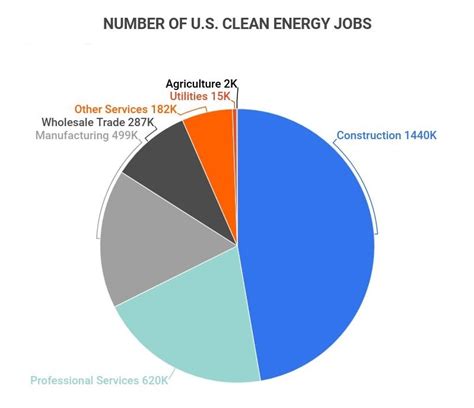
The growth of the renewable energy sector has significantly contributed to job creation across the United States. As the nation shifts toward more sustainable energy sources, the demand for a skilled workforce to facilitate this transition has surged.
According to recent reports, job opportunities in the U.S. Renewable energy sector have expanded rapidly, outpacing many traditional industries. Here are some key points highlighting this impact:
- Employment Growth: The renewable energy industry employed over 3 million people in 2022, with solar and wind energy being the largest contributors.
- Job Diversity: The sector offers a wide range of jobs, from engineering and manufacturing to installation and maintenance, catering to various skill levels.
- Local Economic Boost: Many renewable energy projects are implemented locally, creating jobs that significantly benefit regional economies.
| Renewable Energy Source | Number of Jobs (2022) | Job Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Energy | 250,000 | 20% |
| Wind Energy | 110,000 | 25% |
| Bioenergy | 78,000 | 15% |
| Geothermal Energy | 17,000 | 10% |
Furthermore, the push for a greener economy is incentivizing educational institutions to develop specialized programs. This focus on training for workers in the U.S. Renewable sector ensures a workforce equipped with the necessary skills to thrive in this evolving environment.
In summary, the economic impact of the renewable energy sector extends far beyond job creation. Its influence is felt on local and national levels, driving technological advancements and leading to a more sustainable future.
Technological Innovations Advancing U.S. Renewable Energy Solutions
The landscape of renewable energy in the United States is evolving rapidly, driven by significant U.S. renewable technological innovations. These advancements not only enhance efficiency but also reduce costs, making renewable energy more accessible and appealing to consumers and businesses alike.
Key innovations include:
- Solar Energy Technology: Breakthroughs in photovoltaic cells and solar panel design, such as bifacial solar panels and greater efficiency rates, have led to an increase in solar energy adoption.
- Wind Turbine Development: Innovations in turbine design, including larger blades and higher towers, have increased the energy output of wind turbines, enabling energy generation in areas previously considered unsuitable.
- Energy Storage Solutions: Advanced battery technologies, including lithium-ion and flow batteries, are improving energy storage capabilities, allowing for better management of intermittent energy sources like solar and wind.
- Smart Grid Technology: The deployment of smart grids facilitates improved energy distribution and provides real-time data for energy management, enhancing the reliability of the renewable energy supply.
- Hydrogen Production: Innovations in electrolysis and fuel cells are making hydrogen a more viable green energy source, paving the way for its use in transportation and power generation.
These technological advancements are essential in driving the transition towards a more sustainable and U.S. renewable energy future, contributing to national energy independence and environmental goals.
Challenges Facing The U.S. Renewable Energy Industry Today
The U.S. Renewable energy sector, while experiencing significant growth and innovation, still faces numerous challenges that could hinder its advancement and efficiency. Understanding these challenges is essential for developers, policymakers, and stakeholders involved in the renewable energy landscape.
- Regulatory Barriers: Varying state laws and regulations can create a complex environment for renewable energy projects. Navigating these regulatory frameworks can be time-consuming and costly, particularly for smaller developers.
- Intermittency Issues: Many renewable sources, such as wind and solar energy, are variable in nature. This intermittency can lead to inconsistencies in energy supply, making it crucial to invest in energy storage solutions to maintain a stable grid.
- Infrastructure Needs: The current energy infrastructure was primarily designed for fossil fuels, which means significant upgrades are necessary to accommodate an increased share of U.S. Renewable energy sources. This includes expanding transmission lines and integrating smart grid technology.
- Public Perception: Despite growing acceptance, there are still segments of the public that are resistant to transitioning to renewable sources. Overcoming skepticism and misinformation is vital for gaining broader support.
- Financing Challenges: While investment in renewable energy is increasing, securing financing for projects can remain a hurdle, especially in the early stages where risks are perceived to be higher. Access to capital is crucial for innovation.
- Market Competition: The renewable energy market is becoming increasingly competitive, particularly with low-cost fossil fuels. This competition can affect pricing strategies and market share for renewable energy producers.
- Workforce Development: As the industry grows, there is a pressing need for a skilled workforce capable of meeting the demands of new technologies and systems. Training and education programs will be essential to fill this gap.
Addressing these challenges proactively can pave the way for a more robust and resilient U.S. Renewable energy industry, allowing it to contribute significantly to the nation’s energy goals and climate targets.
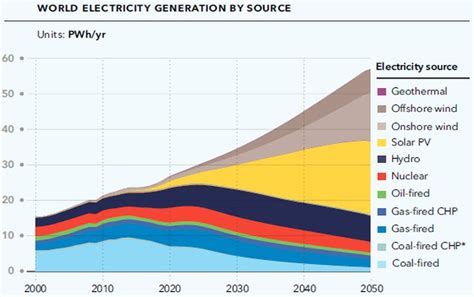
Future Projections For U.S. Renewable Energy Development
As the world increasingly shifts toward sustainable practices, the future of U.S. renewable energy development is projected to be robust and transformative. Experts forecast a significant acceleration in the adoption of renewable energy technologies over the next decade, driven by both policy initiatives and market forces.
By 2030, renewables are expected to represent a larger share of the energy mix, with solar and wind likely leading the charge. Predictions indicate that utility-scale solar installations could double, while wind energy could see similar growth as advancements in turbine technology increase efficiency and reduce costs.
Furthermore, the need for decarbonization to combat climate change is fostering investments in hydrogen production, grid modernization, and energy storage technologies. The integration of these new technologies is anticipated to not only enhance the resilience of the grid but also create a more flexible energy market that can adapt to varying demands.
Government policies, such as incentives for renewable energy investments, emission targets, and support for research and development, are set to play a pivotal role in this transition. Projections suggest that by 2050, up to 70% of the U.S. electricity generation could potentially be derived from renewable sources, significantly reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
The outlook for the U.S. renewable energy sector is bright, with a clear trajectory towards sustainability and growth that promises economic, environmental, and social benefits well beyond this decade.
Frequently Asked Questions
The primary sources of renewable energy in the U.S. include solar power, wind power, hydropower, biomass, and geothermal energy.As of 2023, renewable energy sources provide approximately 20% of the total energy consumption in the U.S.Solar energy has seen significant growth and is one of the fastest-growing sources of renewable energy in the U.S., contributing around 4% to the total electricity generation.Advancements in wind energy technology include larger and more efficient turbines, improved energy storage solutions, and offshore wind farms, which have greatly increased wind energy capacity.Hydropower remains one of the largest sources of renewable electricity in the U.S., contributing about 7% of the total electricity generation and playing a key role in grid stability.Yes, there are several federal incentives, including tax credits and grants, aimed at promoting the development and use of renewable energy technologies.Future trends in U.S. renewable energy include increased adoption of battery storage technology, further investments in offshore wind projects, and a growing emphasis on energy efficiency and smart grid solutions.