Explore the history, advantages, challenges, and future of hydropower as a vital renewable resource for sustainable development and clean energy innovations.In an era where renewable energy sources are gaining unprecedented attention, hydropower remains the unsung hero of clean energy. Often overshadowed by the rapid rise of solar and wind technologies, hydropower has proven to be a reliable and significant player in the global energy landscape for centuries. Harnessing the immense power of flowing water, this sustainable resource not only contributes to reducing carbon emissions but also supports economic growth and community development. In this article, we will explore the rich history of hydropower, delve into its numerous advantages, examine contemporary challenges and innovations, and envision its critical role in achieving a sustainable future. Join us as we uncover why hydropower deserves a prominent place in the discussion of clean energy solutions.
The History Of Hydropower And Its Global Impact
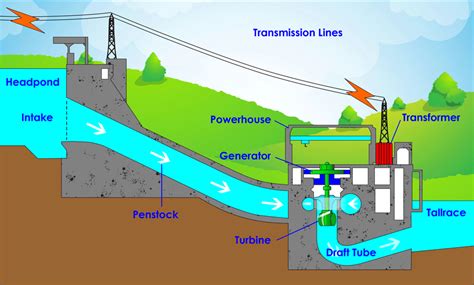
Hydropower has a rich history that dates back thousands of years, showcasing its enduring contribution to human civilization. The earliest recorded use of hydropower can be traced to ancient Greece, where water wheels were employed for grinding grains as far back as 4000 BC. This innovation set a precedent for utilizing flowing water as a power source, paving the way for future developments in the realm of energy.
Throughout history, various cultures have harnessed the potential of water for practical uses. The Romans constructed sophisticated aqueducts and water mills that improved agricultural productivity and industrial processes. By the Middle Ages, water mills were widespread across Europe, emphasizing the significance of hydropower in driving early economies.
Fast forward to the 19th century, the industrial revolution took full advantage of hydropower, facilitating the growth of factories and urban centers. Technologies were developed to generate electricity, leading to the establishment of large-scale hydropower plants. The Great Falls of Paterson in New Jersey, for example, became a hub for hydroelectric power in the early 1800s, marking a pivotal point in integrating hydropower into the electrical grid.
Globally, hydropower has emerged as a cornerstone of renewable energy, providing nearly 16% of the world’s total electricity production today. Countries like China, Brazil, and Canada lead in hydropower generation, benefiting from abundant river systems and favorable topographical conditions. The Three Gorges Dam in China, one of the largest engineering projects in the world, exemplifies the monumental scale and potential of hydropower as a key resource for national energy policies.
Despite its global significance, the discourse around why hydropower should be viewed as a vital component of the clean energy transition often gets overshadowed by emerging technologies such as solar and wind energy. Yet, hydropower remains unmatched in its capacity for large-scale energy storage and grid stability, making it an indispensable player in the race against climate change.
Hydropower’s historical evolution illustrates not only its adaptability but also its critical role in shaping societies and economies worldwide. As nations continue to confront energy demands and environmental sustainability, revisiting why hydropower deserves renewed attention and investment could propel us toward a more resilient and clean energy future.
Advantages Of Hydropower: A Renewable Resource
Why hydropower stands out as a significant player in the renewable energy sector can be attributed to its myriad of advantages. Here are some key benefits of hydropower as a renewable resource:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Source | Hydropower relies on the water cycle, which is replenished naturally, making it a sustainable energy source. |
| Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Unlike fossil fuels, hydropower generation produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a reduced carbon footprint. |
| Energy Storage Capability | Hydropower systems can store energy by pumping water into reservoirs, allowing for energy generation during peak demand times. |
| Job Creation | The development and maintenance of hydropower plants provide numerous jobs and support local economies. |
Additionally, why hydropower is favored in many regions is due to its ability to provide a stable and reliable energy supply. Hydropower plants can operate continuously, unlike some renewable sources that depend on weather conditions. This reliability makes hydropower an essential part of the energy mix, ensuring a consistent power supply for communities.
The advantages of hydropower as a renewable resource are substantial, providing an environmentally friendly, efficient, and sustainable energy option in the transition toward a cleaner energy future.
Why Hydropower Is Essential For Sustainable Development
Why hydropower plays a crucial role in sustainable development is a topic worth exploring, given its potential to address several pressing global challenges. As nations strive to meet their energy needs while minimizing environmental impacts, hydropower stands out as a reliable and clean energy source that can support economic growth and social equity.
One of the primary advantages of hydropower in the context of sustainable development is its ability to provide a stable and renewable energy supply. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, hydropower systems harness the natural flow of water to generate electricity. This transition to renewable energy not only reduces carbon footprints but also fosters energy independence for countries, reducing reliance on imported fuels.
Furthermore, hydropower projects can stimulate local economies by creating jobs and improving infrastructure. The construction and maintenance of dams, turbines, and power plants require a skilled workforce, thereby generating employment opportunities. Additionally, the development of surrounding areas often leads to better roads, schools, and healthcare facilities, contributing to overall community well-being.
Moreover, hydropower can support sustainable agricultural practices by providing irrigation and flood control. Effective water management systems minimize the risks of drought and flooding, ensuring that crops receive adequate water supply while protecting against extreme weather conditions. This balance is vital for food security, especially in regions where agriculture is the primary source of livelihood.
In supporting vulnerable populations, hydropower can enhance energy access in rural areas, facilitating the development of essential services such as healthcare and education. Reliable electricity directly contributes to improved living standards, allowing communities to prosper. By prioritizing access to clean energy through hydropower, nations can take significant strides towards achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to clean water, affordable energy, and economic growth.
Hydropower is integral to sustainable development due to its renewable nature, economic benefits, support for food security, and contribution to energy access. Recognizing these factors emphasizes the importance of investing in hydropower as a viable solution to not only fight climate change but also promote global equality and prosperity.
Challenges Facing Hydropower Projects Today
Despite its vast potential, why hydropower remains a complex endeavor that faces numerous challenges. These issues can hinder the development of new projects and the sustainability of existing ones. Some of the primary challenges include:
- Environmental Concerns: Hydropower projects can lead to significant environmental impacts. The construction of dams often disrupts local ecosystems, fish migration patterns, and water quality. Balancing energy needs with ecological preservation is a significant hurdle.
- High Initial Costs: Although hydropower offers long-term benefits, the upfront investment for building dams and associated infrastructure can be substantial. Securing funding and navigating financial risks often complicates the initiation of new projects.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Hydropower projects face strict regulations and lengthy approval processes. Navigating local, regional, and national policies can create delays, increase costs, and limit project viability.
- Climate Change Impacts: Changes in precipitation patterns and extreme weather events can affect river flows essential for hydropower generation. Adapting to these unpredictable climate conditions is critical for maintaining the efficiency of hydropower systems.
- Social Impacts: Many hydropower projects can displace communities and alter traditional ways of life. Addressing the social implications and gaining community support is vital for project acceptance and long-term success.
Understanding and overcoming these challenges is crucial for maximizing the potential of hydropower as a key player in the clean energy landscape.
Innovative Technologies Enhancing Hydropower Efficiency
As the world seeks to harness clean energy sources, innovative technologies play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of hydropower systems. These advancements not only improve energy output but also ensure that hydropower remains a competitive player in the renewable energy sector.
One significant innovation is the development of high-efficiency turbines. Traditional turbines often face limitations that hinder their performance in varying water flows. New turbine designs, such as the bulb turbine and Kaplan turbine, offer improved efficiency, even under low water conditions, thereby maximizing the energy extracted from available water resources.
Additionally, the integration of smart grid technologies enhances the operational efficiency of hydropower plants. By utilizing real-time data analytics and monitoring systems, operators can optimize energy production based on demand patterns. This facilitates a smoother integration of hydropower into the wider energy grid, promoting stability and reliability.
Another noteworthy advancement is the use of hydropower energy storage systems, particularly pumped storage hydroelectricity (PSH). This technology allows facilities to store excess energy generated during peak times and release it during high-demand periods. It acts as a balancing mechanism, which is vital for managing the intermittent nature of other renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
Furthermore, environmental flow management technologies are being introduced to address ecological concerns associated with hydropower projects. These systems ensure that downstream ecosystems receive adequate water flow, thus minimizing the impact on aquatic habitats while still optimizing energy production.
Overall, as the demand for sustainable energy sources continues to grow, the ongoing development and implementation of innovative technologies are essential. These advancements not only reiterate the importance of why hydropower should be considered a major player in the clean energy revolution but also pave the way for a more sustainable future.
Case Studies Of Successful Hydropower Implementation
Hydropower has proven to be a viable source of energy across various regions around the globe. By studying successful implementations, we can glean important insights into the potential of this Why hydropower resource. Below are a few notable case studies that highlight successful hydropower projects:
| Project | Location | Capacity (MW) | Year Completed | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three Gorges Dam | China | 22,500 | 2012 | World’s largest power station in terms of installed capacity; flood control, improved river navigation. |
| Itaipu Dam | Brazil/Paraguay | 14,000 | 1984 | One of the most productive hydroelectric facilities; provides more than 75% of Paraguay’s electricity. |
| Mount Hope Hydro Station | United States | 18 | 1985 | Run-of-river hydro project that operates with minimal environmental impact; serves local communities. |
| Bhakra Dam | India | 1,325 | 1963 | Significantly contributes to irrigation and supplies power across northern India. |
These case studies demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of Why hydropower as a sustainable energy source. They provide examples of how hydropower can support not only energy needs but also economic development, environmental management, and disaster mitigation. As we look forward, learning from these examples can inspire more innovative projects that capitalize on the benefits of hydropower while addressing its challenges.
The Future Of Hydropower In The Clean Energy Landscape
As the world increasingly turns towards renewable energy sources to combat climate change, the role of hydropower is poised for a significant renaissance. With its longstanding history and proven effectiveness, why hydropower is rapidly becoming one of the critical players in building a sustainable energy future.
One of the most promising aspects of hydropower is its adaptability. Emerging technologies, such as small modular hydropower systems, provide opportunities for generation even in smaller rivers and streams, making it accessible to diverse geographical regions. This localization of energy production not only reduces transmission losses but also empowers communities by providing them with energy security.
Moreover, hydropower’s ability to provide base-load power complements other renewable resources like solar and wind, which can be intermittent. With the growing integration of energy storage solutions, hydropower can be harnessed to stabilize the grid, ensuring a reliable energy supply even during peak demand times.
Additionally, the potential for advancements such as pumped-storage hydroelectricity and hydrokinetic energy systems continues to expand the possibilities for hydropower. These innovations can enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impacts, making hydropower an even more attractive option for future energy strategies.
As governments and organizations worldwide recommit to stringent climate goals, the outdated perceptions of hydropower as a less desirable energy source need to be reevaluated. The urgent quest for clean energy solutions indicates that why hydropower is far from being a forgotten giant—instead, it holds an indispensable position in our transition to a sustainable energy landscape.
The future of hydropower looks bright, powered by innovation and efficiency. The global community must harness this potential, ensuring that hydropower plays a central role in our collective journey towards a cleaner, more resilient energy future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Hydropower is a renewable energy source that harnesses the energy of flowing or falling water to generate electricity.Hydropower is one of the largest sources of renewable electricity globally, contributing significantly to the energy mix while producing minimal greenhouse gas emissions.Advantages of hydropower include its low operational costs, ability to provide a stable power supply, support for grid stability, and its potential for energy storage through pumped storage systems.While hydropower is cleaner than fossil fuels, it can have environmental impacts such as habitat disruption, changes in water quality, and effects on local ecosystems and fish populations.Hydropower generally has a higher capacity factor compared to solar and wind, meaning it can generate electricity more consistently over time, but its development can be more regionally limited.By replacing fossil fuels with hydropower, we can significantly reduce carbon emissions, making it a crucial element in strategies aimed at combatting climate change.Hydropower is often overlooked due to the prominence of newer technologies like solar and wind, concerns about environmental impacts, and limited awareness of its benefits among policymakers and the public.